A hard fork in Cryptocurrency means a change in specifications. When a hard fork occurs, a new Cryptocurrency is created because it is no longer compatible with the previous one. For example, bitcoin has undergone numerous hard forks, resulting in the creation of new currencies such as “bitcoin cash,” “bitcoin gold,” “bitcoin diamond,” and “bitcoin silver.
So, here is what a hard fork is and what to do when a hard fork occurs.
Know what Blockchain is First
As a prerequisite to understanding a hard fork, it is important to understand blockchain technology.
Blockchain technology is considered to be an important technology for the Cryptocurrency system and plays a central role in the Bitcoin (BTC) system.
Blockchain technology, in brief, is a technology that manages the history of transaction data.
When a Bitcoin (BTC) transaction takes place, the historical transaction data within a certain period of time is stored in a unit called a block. This block incorporates data that reveals a time series and appears as if it is connected to the rest of the chain.
The name “blockchain” is derived from the fact that blocks containing historical transaction data are stored in a series of blocks.
The way the Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain is managed differs from the form in which it is managed by a central host computer or server. It is unique in that it is decentralized and managed by all terminals connected to the Bitcoin system.
Bitcoin (BTC), through its blockchain technology, avoids becoming a centralized currency system where authority is concentrated in the hands of a specific manager. It operates as a decentralized currency system, managed by an unspecified number of people working together.
What is a Hard Fork?
A hard fork is a change in the specifications of a blockchain. A hard fork is a change in the rules of the Cryptocurrency system, so to speak.
When a Cryptocurrency system is made to operate under new rules, the old rules are ignored. From a specific point in time, a chain of blocks generated under the new rules is created.
However, if a hard fork is performed, the blocks with the old rules will also grow into a chain. In other words, the old and new blocks branch off like forks at a dinner table.
Since the blockchain operating under the new rules and the blockchain operating under the old rules are not compatible, the two chains will grow independently of each other.
The key to how far the old and new chains will grow is whether or not it is possible to secure system participants who will continue to support each set of rules.
Hard Fork vs Soft fork
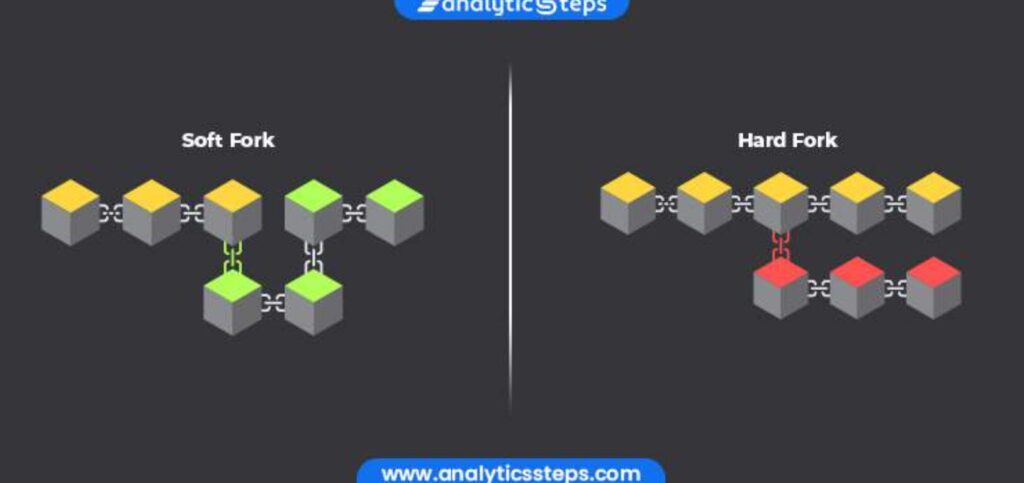
When changes are made to the blockchain specifications, not only hard forks but also soft forks may occur.
Both hard and soft forks are the same in that they change the rules of the Cryptocurrency System. However, the method of applying the rule change is different.
Hard Fork
In the case of a hard fork, the rule change is applied to blocks after a certain point in time, while the old rules are left in place for blocks in the past.
Therefore, it is characterized by the possibility that not only the blockchain based on the new rules but also the blockchain based on the old rules will grow.
Soft Fork
In a soft fork, on the other hand, the rule change is applied to all blocks.
Since the rule change also applies to past blocks generated prior to the time of the change, there is no room for the blockchain to branch out.
Since the old rules will disappear completely, there will be no room for the wishes of Cryptocurrency system participants who supported the old rules.
Hard Fork vs Segwit
Some users interested in Cryptocurrency may have heard of the term Segwit. Segwit, to put it simply, is a technology that compresses Cryptocurrency transaction data, thereby reducing the amount of data.
The background behind the need for the Segwit technology was the issue of the block size of Bitcoin (BTC).
Since there is an upper limit to the storage size of a single block in the blockchain, there was concern that as the volume of Bitcoin (BTC) transactions increased, it would become impossible to store all of the transaction data.
Segwit was created as a solution to this block size problem by using a technology that changes the compression method of the data to be written to the block. The introduction of Segwit is a change to the blockchain specifications.
However, since it is only a rule change to reduce the transaction size, there is no need for a hard fork, but rather a soft fork.
Why you need Hard Fork?
When a hard fork occurs, the blockchain splits.
This is an event with major consequences for the Cryptocurrency system. Why go to such lengths to implement a hard fork? The purposes of a hard fork include the following
Solving the Scalability Problem
One is to solve scalability problems.
As the volume of Cryptocurrency transactions increases, transaction approvals cannot keep up, resulting in transaction delays and higher fees. This is the scalability problem.
Here, changing the specifications, such as changing the block size, can solve this problem. However, if there are many users who support the old rules, it is difficult to perform a soft fork.
In such cases, a hard fork will be performed.
Disabling hacking activities
The other reason is to change specifications, such as disabling hacking activities.
In some Cryptocurrencies, a hard fork can be performed to nullify the hacked Cryptocurrency, thereby pretending that no damage was done.
History of Hard Fork
In past hard forks, a new Cryptocurrency has been created by stretching a branching new rules-applied blockchain.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
A prime example is the creation of Bitcoin Cash (BCH), which was created in August 2017 through a hard fork from Bitcoin (BTC).
The reason for the hard fork was a specification change aimed at resolving scalability issues. The change expanded the capacity of a block from 1MB (megabyte) to 8MB.
Ethereum Classic (ETC)
In June 2016, Ethereum (ETH) also split into Ethereum Classic (ETC) and Ethereum (ETH) by a hard fork.
The hard fork was caused by the the DOA incident. the DOA is the name of the project, which was the victim of a hack that led to the hard fork.
The problem was not with the main body of the Ethereum system (ETH), but with a subprogram recorded in a feature called smart contracts.
As a result, the specifications were changed to improve security, but those who supported the old blockchain who did not agree with the changes continued to grow the block, leading to the creation of a new currency called Ethereum Classic (ETC).
Advantages of Hard Fork
The main advantages of a hard fork being performed include the following
Problems solution.
The first is the possibility of solving problems with the blockchain and other issues.
Issues that the blockchain faces, such as scalability problems, can be improved through specification changes. 2.
Granting New Currency
Second, when a hard fork occurs, a new currency is created, and users who held the currency before the split may be granted the new currency free of charge.
Holders of the pre-branch currency may be able to obtain the new currency without effort. 3.
Price Rising
Third, if there is demand for the newly created Cryptocurrency, the price can be expected to rise. Generally, new currencies created by hard forks are in constant demand because of some systemic improvement.
Theoretically, if the currency is simply split, the sum of the old and new currency values would not change. However, the currency value may increase as demand increases due to the improvements.
The advantage is that if users who held the currency before the split are granted the new currency, the value of their property may increase.
Disadvantages of Hard Fork
Hard forking has disadvantages as well as advantages.
One of the disadvantages, for example, is that hash power is distributed. Hash power can be understood as the machine power required to approve a block.
In a situation where a large amount of machine power is required to successfully approve a transaction, the accuracy of the transaction approval will increase. However, after a hard fork, the machine power used for the approval process will be distributed, resulting in a less difficult approval process and possibly a decrease in transaction approval accuracy.
The negative effects of lower transaction accuracy include, for example, the following
Replay attacks
The first is an increase in the risk of attacks, known as replay attacks.
Replay attacks are attacks in which the transfer of data such as money transfer information is illegally repeated or delayed. By lowering hash power, the risk of being exposed to such attacks increases. 2.
Risk of Bugs and Errors
The second is the increased risk of bugs and errors. This is also closely related to the decrease in hash power. 3.
Reliability of Transaction Data
The third is a decrease in the reliability of transaction data. This risk is caused by the reduced difficulty of the approval process.
What to Prepare When Hard Fork occurs
When a hard fork is scheduled to take place, the following points should be careful when conducting transactions.
Abrupt price fluctuations
First, there is the possibility of sudden price fluctuations.
Before and after a hard fork, there will be various speculations about the demand for the old and new currencies. Also, some users trade to see if the improvements applied to the new currency will work well.
Therefore, prices can fluctuate significantly depending on the status of the hard fork.
Temporary suspension of trading by exchanges
Another point to note is that exchanges may halt trading of the old and new target currencies before and after the hard fork.
Exchanges will also need to determine whether the blockchain of the new currency can be successfully stretched and trading can continue.
It is also necessary to determine whether the new currency will be granted automatically. Be sure to check for information on the suspension of trading transactions and remittances during a certain period of time before and after a hard fork.
What happens to your Crypto
Some users who hold pre-split currency may be concerned about what will happen to their currency if a hard fork occurs.
They may also be concerned about whether or not they will automatically be granted the new currency. In past hard forks, new currency was automatically granted to holders of pre-split currency.
In the case of an automatic grant, no particular procedure is required on the part of the investor, and the balance of the new currency will be increased automatically. In addition, there is no need to worry about the old currency, as the amount of the old currency held will be maintained.
However, it is important to understand that the new currency will not always be granted. In fact, there have been many cases where new currency was not granted.
Do not expect too much for the new currency to be granted. It is also necessary to be aware that the response to the granting of new currency may differ from one exchange to another.
Summary
When a hard fork occurs, there are some advantages, such as improvements to the Cryptocurrency system and the automatic granting of currency.
However, there may also be some disadvantage associated with a reduction in hashing power. In some cases, exchanges may take measures to suspend transactions or transfers for some time.
Therefore, it is important to keep such risks in mind and prepare for the hard fork in advance. Once a hard fork is announced, make sure to gather information and secure your trading environment.

